Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Topic Contents
Molluscum Contagiosum
Condition Basics
What is molluscum contagiosum?
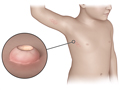
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection that causes small pearly or flesh-colored bumps. The center of the bump is often indented. The infection is caused by a virus. The virus is easily spread but is not harmful.
This infection is most common in children. But teens and adults can also get it, often from taking part in sports like wrestling and gymnastics or from sexual contact. It can occur in healthy people. But when it occurs in people with a weak immune system, the symptoms may be worse.
How does it spread?
The molluscum contagiosum virus commonly spreads through skin-to-skin contact. This includes sexual contact or touching the bumps and then touching the skin. Touching an object that has the virus on it, such as a towel, also can spread the infection.
The virus can spread from one part of the body to another. Or it can spread to other people, such as among children at day care or school. The infection is contagious until the bumps are gone.
The time from exposure to the virus until the bumps appear usually is 2 to 7 weeks. But in some cases it can take up to 6 months.
What are the symptoms?
Molluscum contagiosum causes small pearly or flesh-colored bumps that don't cause pain. The bumps are round with a dimple in the center. They may itch, become inflamed, and turn reddish as your body fights the virus.
How is it diagnosed?
To diagnose molluscum contagiosum, your doctor will do a physical exam and may take a sample of the bumps for testing. If you have bumps in your genital area, your doctor may check for other sexually transmitted infections, such as genital herpes.
How is molluscum contagiosum treated?
Molluscum contagiosum doesn't usually need to be treated. The infection usually goes away within 6 to 18 months.
But people sometimes ask that the condition be treated, especially if it lasts a long time—the bumps can sometimes last for several years. And doctors usually recommend treatment for any bumps in the genital area to prevent spread to sexual partners. People with weakened immune systems also are usually treated.
If you have treatment, your choices may include:
- Freezing the bumps. This is called cryotherapy or cryosurgery.
- Scraping off the bumps. This is called curettage.
- Putting medicine on the bumps. Some medicines, such as cantharidin, are applied by the doctor. Other medicines are applied at home by the patient.
You may choose to not have your child treated. But if your child has treatment, talk to the doctor about how to prevent pain, scarring, and changes in skin color (pigment) from treatment.
How can you prevent it?
To prevent molluscum contagiosum from spreading:
- Wash your hands.
- Try not to touch, scratch, or pick at the bumps.
- Cover the bumps with a bandage, medical tape, or clothing when around other people.
- Don't share towels or washcloths.
- Don't shave the area where you have bumps.
- If the bumps are in your genital area, avoid sexual contact.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: December 4, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: December 4, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.